Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ikeda, Yuji*; Soriano, J. K.*; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.4828_1 - 4828_9, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:97.94(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institutes of Natural Sciences*
JAEA-Review 2022-059, 34 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of the continuous monitoring of tritium water by mid-infrared laser spectroscopy" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to demonstrate the principle of short-time measurement of tritiated water at the "60 Bq/cc level" using a cavity ring-down measurement system with a mid-infrared laser. In order to achieve the above goal, (1) research on the cavity ring-down system and (2) evaluation of hydrogen isotope composition under environmental conditions and preparation of standard samples (subcontractor: Hirosaki University) were conducted this fiscal year. In (1), a mid-infrared cavity ring-down test was conducted. An optical bench (3 m  1.2 m) was set up in the laboratory, …
1.2 m) was set up in the laboratory, …
Batsaikhan, M.; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Saeki, Morihisa*; Karino, Takahiro; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 13 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-015, 119 Pages, 2022/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Analysis of microparticles generated by laser processing and development of a methodology for their nuclear identification" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. Although laser processing has various advantages, one well-known disadvantage is that it generates a large amount of microparticles during the processing. Therefore, the application of laser processing to decommissioning waste contaminated with radioactive materials has been hesitant because the mechanism generating the microparticles has not been fully understood.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-007, 59 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Identification of altered phases of fuel debris by laser fluorescence spectroscopy" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to identify alteration phases occurring on the surface fuel debris at various conditions, using time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS), which is a selective analytical technique for U(VI), a major constituent of fuel debris and stable in oxidizing conditions.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-lab*
JAEA-Review 2021-027, 62 Pages, 2021/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted in FY2020. Although LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) is commercially available for application to remote composition measurement, it is not suitable for high radiation environment due to loss in optical fibers derived from the influence of radiation, reduction in laser transmission output, and nuclear fuel debris properties. There are general concerns of the signal strength decrease. In addition, since LIBS is generally considered to be unsuitable for isotope measurement, there are problems to be improved.
Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo; Tanabe, Rie*; Ito, Yoshiro*
Optics Express (Internet), 29(4), p.5205 - 5212, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:84.11(Optics)Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) combined with liquid jets was applied to the detection of trace sodium (Na) in aqueous solutions. The sensitivities of two types of liquid jets were compared: a liquid cylindrical jet with a diameter of 500  m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20
m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20  m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57
m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57  g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5
g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5  g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2020-053, 64 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Identification of Altered Phases of Fuel Debris by Laser Fluorescence Spectroscopy" conducted in FY2019.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2020-031, 69 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Analysis of microparticles generated by laser processing and development of a methodology for their nuclear identification" conducted in FY2019.
Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(6), p.062001_1 - 062001_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.16(Physics, Applied)Using a semiconductor microwave source and a coaxial cable for microwave transmission, a compact microwave-assisted, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system without a microwave cavity or waveguide was developed. Several types of electrode heads were tested, so that the emission intensity was 50 times larger than without microwave. The limit of the enhancement effect was also found.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2019-034, 59 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, conducted the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aimed to contribute to solving problems in the field of nuclear energy represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development was promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barriers of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Analysis of microparticles generated by laser processing and development of a methodology for their nuclear identification". Although laser processing has various advantages, one well-known disadvantage is that it generates a large amount of microparticles during the processing. Therefore, the application of laser processing to decommissioning waste contaminated with radioactive materials has been hesitant because the mechanism generating the microparticles has not been fully understood. In this study, the mechanism of microparticle production by laser processing is investigated from fundamentals. Also, we develop a laser on-line principle device to examine the nuclides present in the microparticles that are produced, based on the measurement of the particle size distribution by collecting the microparticles using aerodynamic lenses.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2019-030, 66 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Identification of Altered Phases of Fuel Debris by Laser Fluorescence Spectroscopy". In the present study, we focus on uranium that is the main component element in debris, and identify the altered phase produced on the debris surface under various conditions by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) with high sensitivity to hexavalent uranium (U(VI)) that is stable in oxidation environment. In particular, further high-sensitive and high-resolution measurements are implemented by improving the fluorescence yields and suppressing the broadening of the peaks through the measurements at ultra-low temperature. In addition, with the supports by quantum chemical calculations, multivariate analysis, and machine learning, the method will lead to the identification of multicomponent and heterogeneous altered phase of fuel debris.
Chrysalidis, K.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Ahmed, R.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ballof, J.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Harding, R. D.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 463, p.472 - 475, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.72(Instruments & Instrumentation)A number of radiogenically produced dysprosium isotopes have been studied by in-source laser spectroscopy at ISOLDE using the Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source (RILIS). Isotope shifts were measured relative to  Dy in the
Dy in the 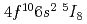 (gs)
(gs) 
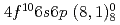 (418.8 nm
(418.8 nm 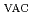 )resonance transition. The electronic factor,
)resonance transition. The electronic factor, 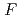 , and mass shift factor, M, were extracted and used for determining the changes in mean-squared charge radii for
, and mass shift factor, M, were extracted and used for determining the changes in mean-squared charge radii for 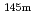 Dy and
Dy and 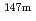 Dy for the first time.
Dy for the first time.
Abe, Yuta; Otaka, Masahiko; Okazaki, Kodai*; Kawakami, Tomohiko*; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/05
Since the hardness of fuel debris containing boride from B C pellet in control rod is estimated to be two times higher as that of oxide, such as UO
C pellet in control rod is estimated to be two times higher as that of oxide, such as UO and ZrO
and ZrO , it is necessary to select the efficient and appropriate operation for removal of fuel debris formed in the severe accident of nuclear power plants. We focused on the characteristics of LIBS, an innovative rapid chemical in-situ analysis technology that enables simultaneous detection of B, O, and other metal elements in fuel debris. Simulated solidified melt specimens were obtained in the plasma heating tests (CMMR-0/-2, performed by JAEA) of simulated fuel assembly (ZrO
, it is necessary to select the efficient and appropriate operation for removal of fuel debris formed in the severe accident of nuclear power plants. We focused on the characteristics of LIBS, an innovative rapid chemical in-situ analysis technology that enables simultaneous detection of B, O, and other metal elements in fuel debris. Simulated solidified melt specimens were obtained in the plasma heating tests (CMMR-0/-2, performed by JAEA) of simulated fuel assembly (ZrO is used to simulated UO
is used to simulated UO pellet, other materials such as stainless steel, B
pellet, other materials such as stainless steel, B C are same as fuel assembly). The LIBS signals of (B/O)/Zr ratio showed good linear relationship with Vickers hardness. This technique can be also applied as in-situ assessment tool for elemental composition and Vickers hardness of metal-oxide-boride materials.
C are same as fuel assembly). The LIBS signals of (B/O)/Zr ratio showed good linear relationship with Vickers hardness. This technique can be also applied as in-situ assessment tool for elemental composition and Vickers hardness of metal-oxide-boride materials.
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Keisuke; Wakaida, Ikuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
A high-radiation resistant optical fiber has been developed in order to investigate the interiors of the reactor pressure vessels and the primary containment vessels at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The tentative dose rate in the reactor pressure vessels is assumed to be up to 1 kGy/h. We developed a radiation resistant optical fiber consisting of a 1000 ppm hydroxyl doped pure silica core and 4 % fluorine doped pure silica cladding. We attempted to apply the optical fiber to remote imaging technique by means of fiberscope. The number of core image fibers was increased from 2000 to 22000 for practical use. The transmissive rate of infrared images was not affected after irradiation of 1 MGy. No change in the spatial resolution of the view scope by means of image fiber was noted between pre- and post-irradiation. We confirmed the applicability of the probing system, which consists of a view scope using radiation-resistant optical fibers.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
Matsumoto, Ayumu
Reza Kako Gakkai-Shi, 23(3), p.222 - 231, 2016/10
no abstracts in English
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2016-005, 40 Pages, 2016/05
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of natural uranium of wavelength ranging from 470 to 670 nm. The 173 atomic spectra and 119 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
 on Na-montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modeling
on Na-montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modelingSasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Saito, Takumi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Takagi, Ikuji*; Kimura, Takaumi; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.592 - 601, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.37(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influences of pH and the concentrations of Eu and NaNO
and NaNO on the sorption of Eu
on the sorption of Eu to Na-montmorillonite were investigated through batch sorption measurements and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The pH had a little effect on the distribution coefficients (Kd) in 0.01 M NaNO
to Na-montmorillonite were investigated through batch sorption measurements and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The pH had a little effect on the distribution coefficients (Kd) in 0.01 M NaNO , whereas the Kd strongly depended on pH at 1 M NaNO
, whereas the Kd strongly depended on pH at 1 M NaNO . A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was successfully applied to the measured Kd. The TRLFS spectra of Eu
. A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was successfully applied to the measured Kd. The TRLFS spectra of Eu sorbed were processed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), which corresponded to one outer-sphere (factor A) and two inner-sphere (factor B and C) complexes. It turned out that factors A and B correspond to Eu
sorbed were processed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), which corresponded to one outer-sphere (factor A) and two inner-sphere (factor B and C) complexes. It turned out that factors A and B correspond to Eu sorbed by ion exchange sites and inner-sphere complexation with hydroxyl groups of the edge faces, respectively. Factor C became dominant at relatively high pH and ionic strength and likely correspond to the precipitation of Eu(OH)
sorbed by ion exchange sites and inner-sphere complexation with hydroxyl groups of the edge faces, respectively. Factor C became dominant at relatively high pH and ionic strength and likely correspond to the precipitation of Eu(OH) on the surface.
on the surface.